Lumps can form on different parts of the body due to various underlying reasons. While some are harmless, others may indicate a more serious condition. Identifying the cause of a lump is crucial for proper management and treatment.
Common Causes of Lumps
- Cysts: Fluid-filled sacs that form due to blocked glands, infections, or other bodily processes. Most are benign but can become painful or infected.
- Lipomas: Soft, movable lumps made of fatty tissue. They are generally harmless but may cause discomfort if they press on nerves or muscles.
- Infections: Abscesses, which are pus-filled lumps caused by bacterial infections, often require drainage or antibiotics.
- Tumors and Cancer: While most lumps are benign, some may indicate malignancies. Hard, fast-growing lumps or those accompanied by pain or skin changes should be evaluated promptly.
If you notice an unexplained lump, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
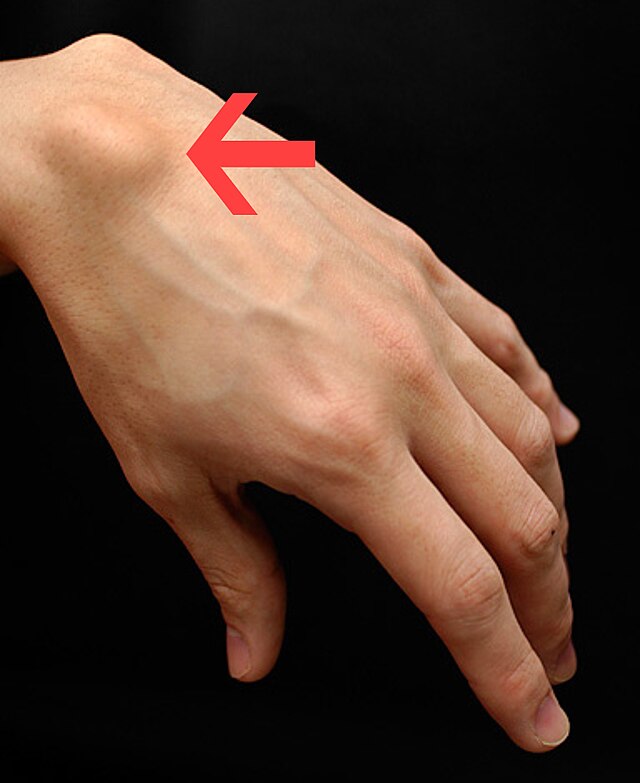
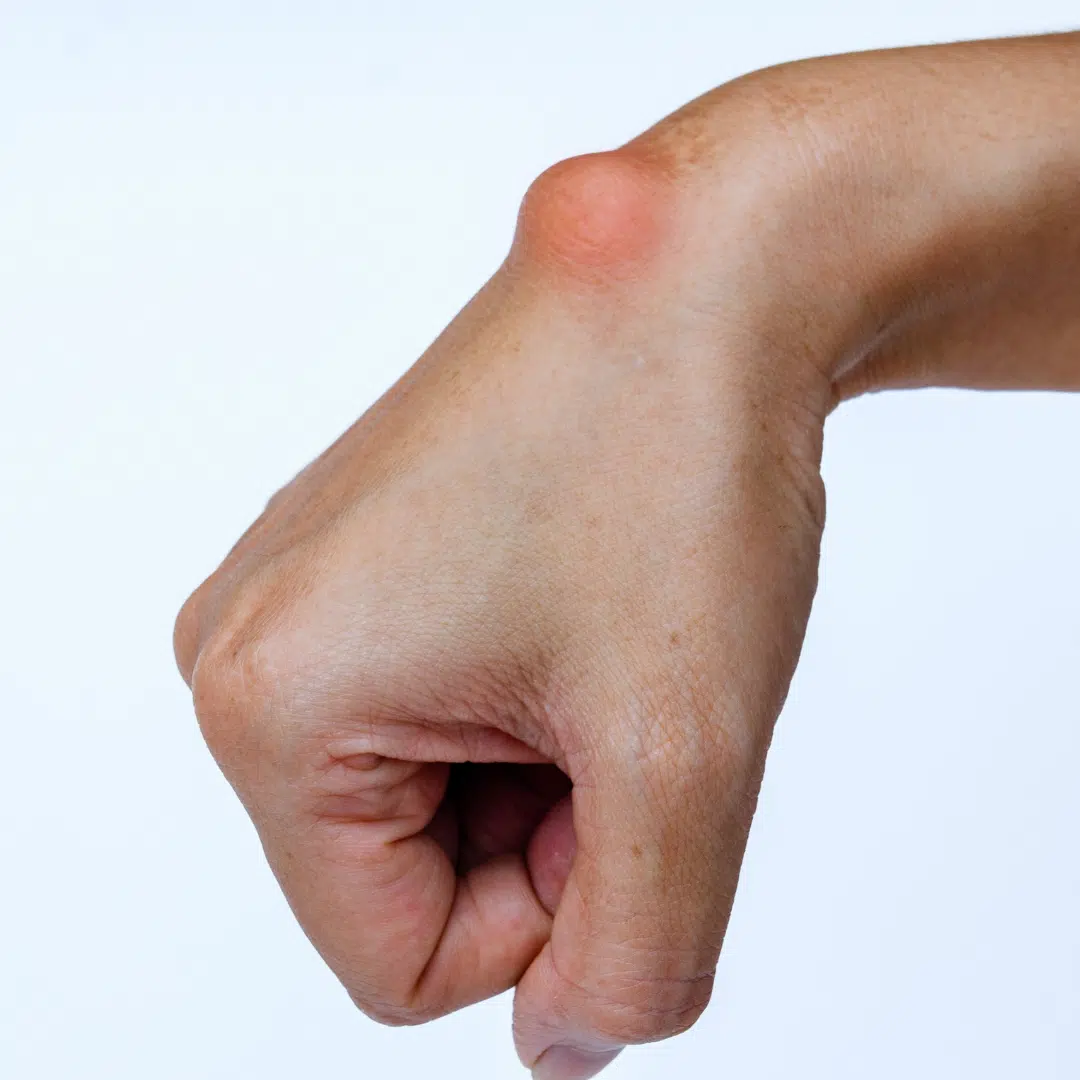
Lumps on the Wrist or Hand: Possible Causes
Lumps on the wrist or hand are often non-serious but can sometimes indicate underlying health conditions. Here are some common causes:
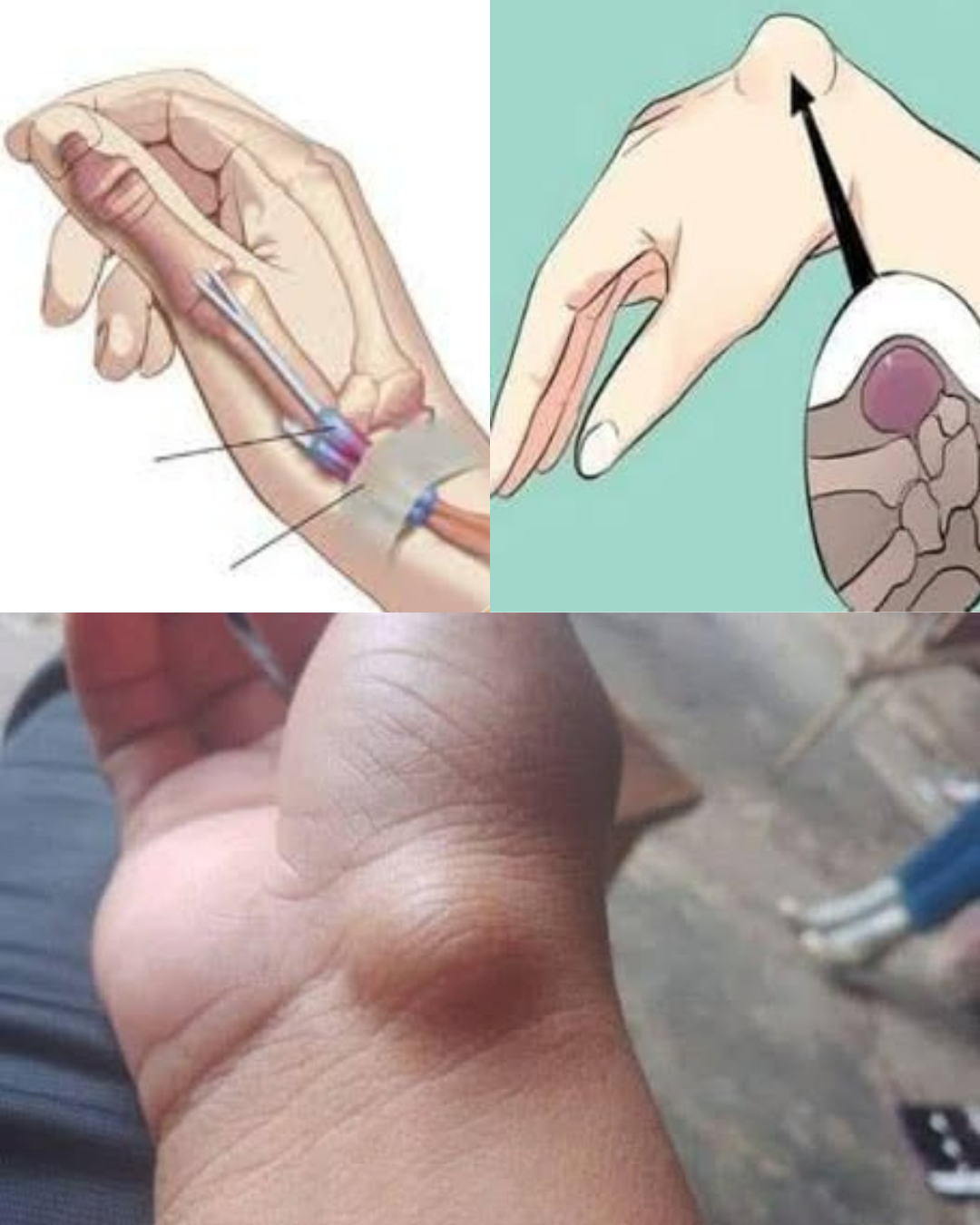
- Ganglion Cyst: A non-cancerous, fluid-filled lump that appears near joints or tendons, often on the back of the wrist or hand. It may fluctuate in size and sometimes cause discomfort if pressing on a nerve.
- Giant Cell Tumor of the Tendon Sheath (GCTTS): A slow-growing, benign tumor that forms in the tendon sheath. It is usually painless.
- Epidermal Inclusion Cyst: A lump under the skin filled with keratin, often resulting from irritation or injury. It may become inflamed or infected.
- Malignant Tumors: Although rare, some fast-growing, painful lumps may be cancerous, such as melanoma or sarcomas.
- Other Tumors: Less common benign growths include lipomas (fatty tumors), neuromas (nerve tumors), and fibromas (connective tissue tumors).
Lumps Related to Joint and Autoimmune Conditions
- Osteoarthritis: Wear and tear of cartilage can cause small bony lumps on finger joints, accompanied by pain and swelling.
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA): This autoimmune disease can cause firm, painless lumps (rheumatoid nodules) near affected joints.
- Gout: A type of arthritis caused by uric acid buildup, leading to painful joint swelling. Hard, white lumps called tophi may form under the skin.
Other Possible Causes
- Foreign Body Reaction: A splinter or glass fragment stuck in the hand can cause swelling and a visible lump.
- Carpal Boss: A bony overgrowth on the back of the wrist, sometimes mistaken for a ganglion cyst, which may cause arthritis-like pain.
- Trigger Finger: Swollen flexor tendons can create a lump at the base of a finger, making it difficult to move.
- Dupuytren’s Contracture: Thickening of the palm tissue can form firm lumps, leading to bent fingers over time.
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical attention if a lump:
- Grows rapidly
- Causes pain or discomfort
- Is associated with numbness, tingling, or weakness
- Shows signs of infection (redness, warmth, pus)
- Is frequently irritated due to its location
Diagnosis and Treatment
Doctors may use the following methods to diagnose a lump:
- Physical Examination: Checking for pain, tenderness, or fluid-filled vs. solid masses.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound, MRI, or X-rays to assess the lump’s structure.
- Biopsy: Extracting a tissue sample for further analysis if a tumor is suspected.
- Laboratory Tests: Blood tests to check for conditions like RA or gout.
While most lumps are harmless, early diagnosis ensures proper treatment and prevents complications. If you have concerns about a lump, consult a doctor for evaluation.