Vitamin B12 is an essential nutrient that plays a crucial role in red blood cell formation, neurological function, and DNA synthesis. A deficiency can lead to serious health issues, so understanding its symptoms, causes, and dietary sources is important.
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
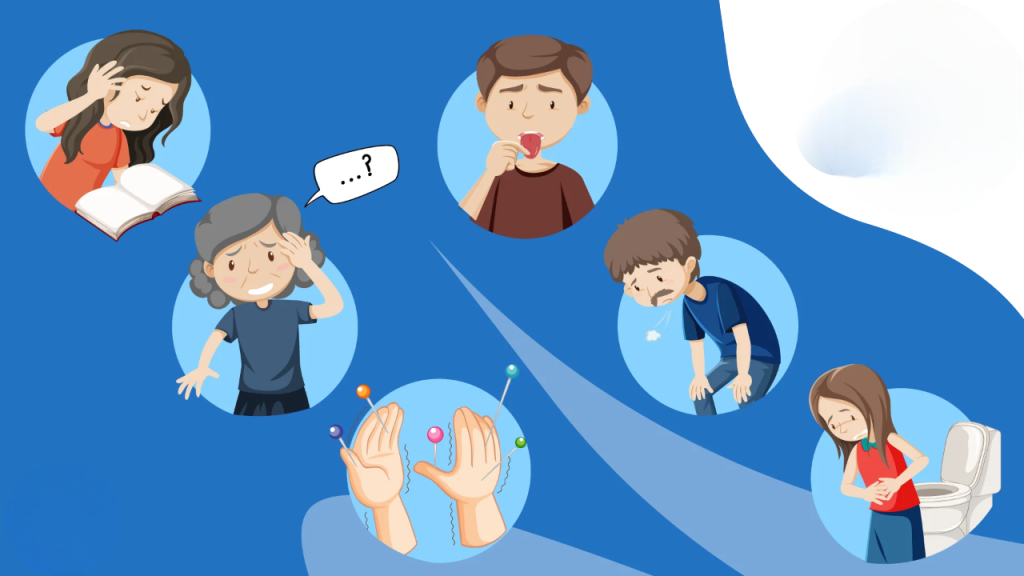

- Anemia: A lack of vitamin B12 can cause megaloblastic anemia, leading to fatigue and weakness.
- Fatigue and Weakness: People with low B12 levels often experience chronic tiredness and lack of energy.
- Neurological Issues: Symptoms such as numbness, tingling in the hands and feet, balance problems, and nerve damage may occur.
- Breathlessness and Heart Palpitations: Severe deficiency may cause irregular heartbeats and shortness of breath.
- Cognitive Issues: Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, and brain fog can be linked to low B12 levels.
Causes of Vitamin B12 Deficiency
- Dietary Deficiency: Those following a strict vegetarian or vegan diet may lack B12, as it is primarily found in animal-based foods.
- Malabsorption Issues: Conditions such as gastritis, Crohn’s disease, celiac disease, and pernicious anemia can impair the body’s ability to absorb vitamin B12.
- Aging: Older adults may have reduced stomach acid levels, which are necessary for B12 absorption.
Best Dietary Sources of Vitamin B12
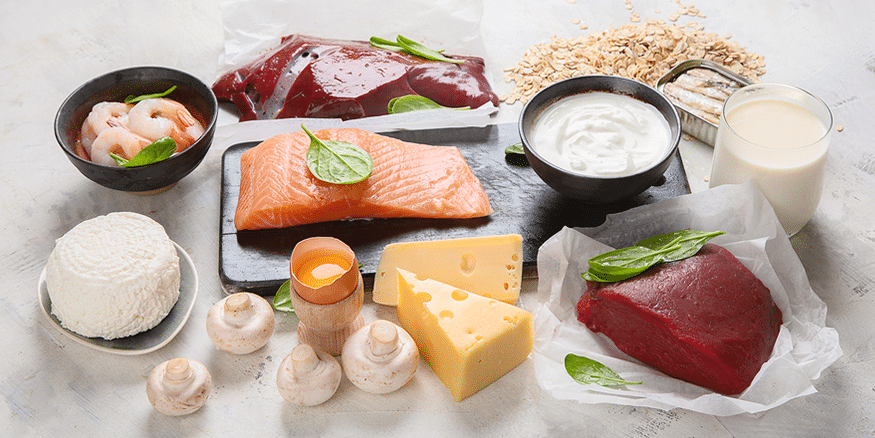

To maintain adequate levels of vitamin B12, consider consuming the following foods:
- Organ Meats: Liver (especially beef or lamb liver) is one of the richest sources of vitamin B12.
- Shellfish: Clams, mussels, and oysters contain high amounts of B12.
- Fish: Salmon, tuna, and trout are excellent sources.
- Beef: Lean cuts of beef provide a good amount of vitamin B12.
- Dairy Products: Milk, cheese, and yogurt contain moderate levels of B12.
- Eggs: A valuable source of B12, especially in the yolk.
- Fortified Foods: Some breakfast cereals, plant-based milks, and nutritional yeasts are fortified with B12.
Conclusion
Vitamin B12 is essential for overall health, particularly for red blood cell production and neurological function. A deficiency can lead to serious health complications, so it is important to consume adequate amounts through diet or supplements if necessary. Those at risk, such as vegetarians, older adults, and individuals with digestive disorders, should monitor their B12 levels and consult a healthcare professional if symptoms arise. Maintaining a balanced diet with B12-rich foods is the best way to prevent deficiency and support long-term health.